Exploring Ancient Chinese Hygiene Practices: Bathing and Beyond
What Did Ancient Chinese Use to Bathe?
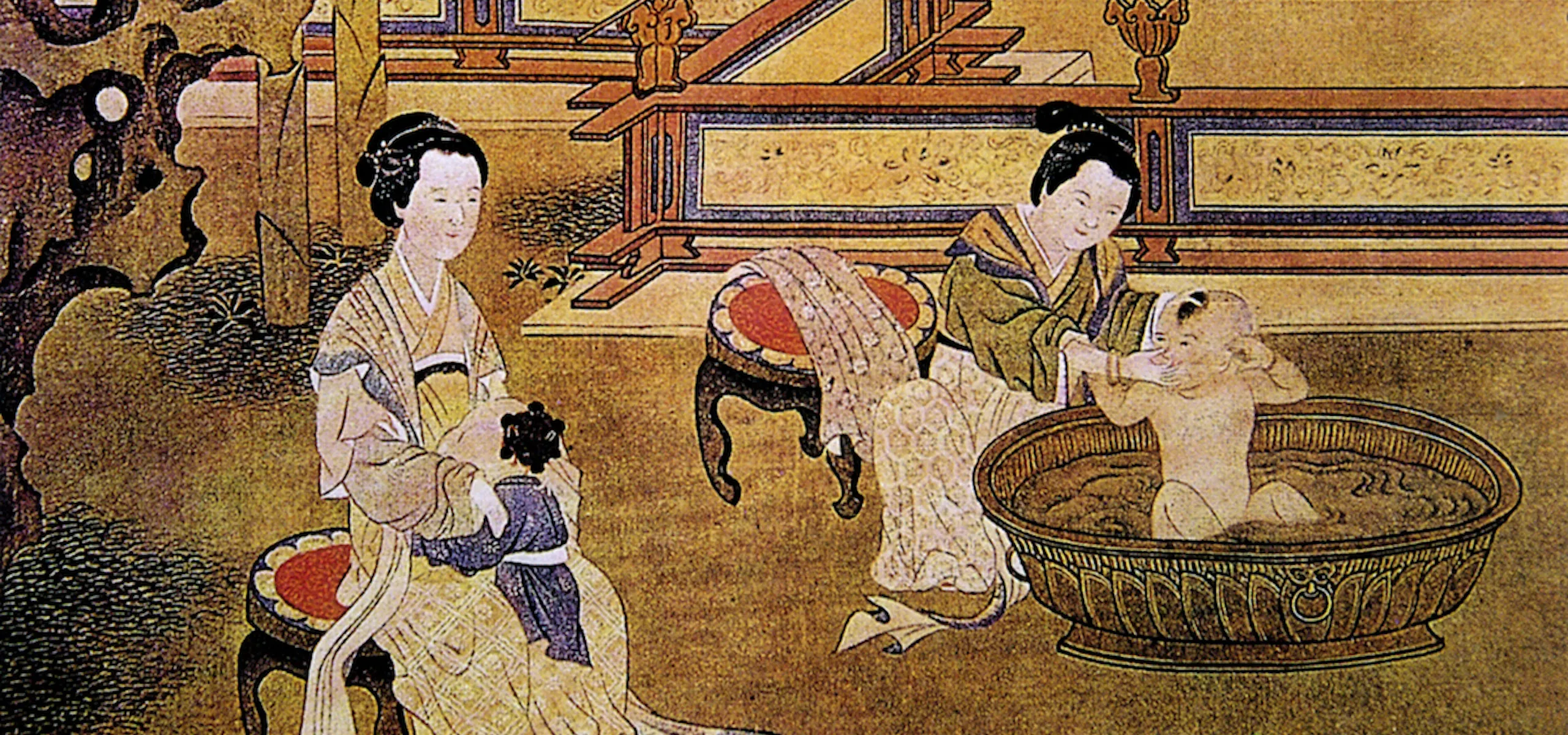
Hygiene has always played a crucial role in human societies, and ancient China is no exception. The ancient Chinese employed a variety of materials and methods to maintain cleanliness, which reflected their cultural beliefs and social norms. Bathing was not merely a matter of personal hygiene; it was intertwined with rituals, health practices, and philosophical ideals.
Common Bathing Materials and Methods
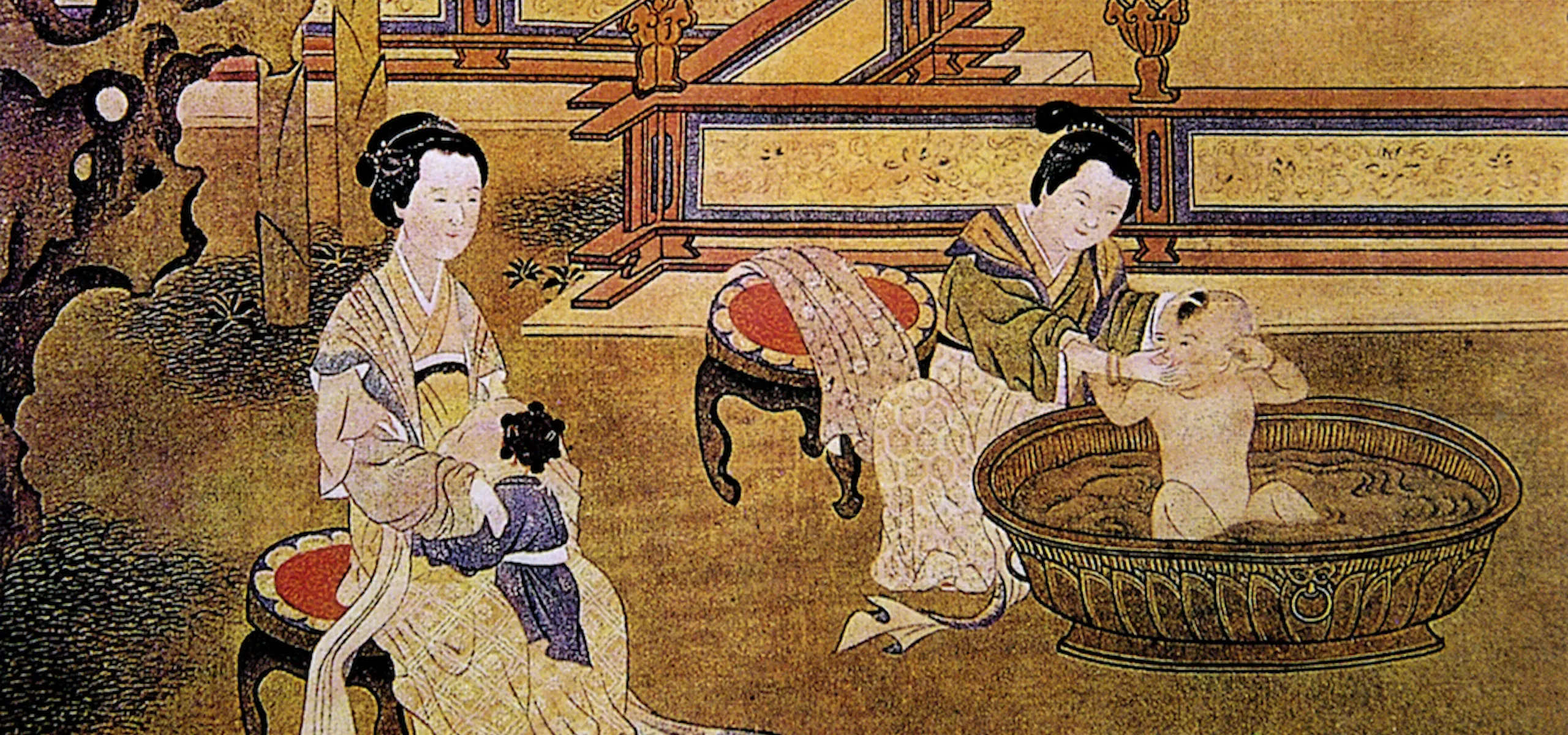

In ancient China, bathing practices varied across different regions and dynasties, influenced by climate, available resources, and cultural practices. Here are some common materials and methods used for bathing:
- Water Sources:
- Rivers and Streams: Freshwater sources were the primary means for bathing. The ancient Chinese often sought clean rivers or streams, believing that flowing water had purifying qualities.
- Rainwater: Collected rainwater was also used, especially in areas where freshwater sources were scarce.
- Herbs and Oils:
- Ancient Chinese often added herbs to their baths, which were believed to have therapeutic properties. Ingredients like ginger, lotus, and mint were commonly used.
- Essential oils extracted from plants were also added for fragrance and purported health benefits.
- Bathing Tools:
- Bamboo Scrubbers: A simple yet effective tool, bamboo scrubbers helped to exfoliate the skin.
- Clay and Mud: Some regions used mud from riverbanks for its exfoliating and purifying properties, while others favored clay masks for skin health.
Types of Baths

The ancient Chinese had various bathing practices, each with its own significance:
- Public Baths:
- Public baths were common in larger cities, providing a social space for people to gather and cleanse themselves. These baths often featured communal pools filled with warm water, promoting social interaction alongside hygiene.
- Private Baths:
- Wealthier families often constructed private bathing facilities, incorporating heated water and herbal infusions, signifying status and refinement.
- Ritual Baths:
- Certain bathing practices were tied to rituals and religious observances, symbolizing purification before significant events or festivals.
The Evolution of Hygiene Practices Over Time
Influences from Different Dynasties
The hygiene practices in ancient China evolved significantly over the centuries. Various dynasties influenced these practices through their cultural exchanges, technological advancements, and philosophical ideals.
- Han Dynasty (206 BCE – 220 CE):
- The Han dynasty saw the promotion of public health measures, including improved sanitation practices.
- Tang Dynasty (618 – 907 CE):
- The Tang dynasty was known for its luxurious public baths, influenced by cultural exchanges with the Silk Road. Bathhouses became centers for socializing and cultural exchange.
- Ming Dynasty (1368 – 1644):
- The Ming dynasty emphasized personal hygiene, leading to the development of private bathing facilities and the use of specialized bathing tools.
Impact of Cultural Exchanges on Hygiene
Interactions with neighboring cultures, such as those from India and Persia, also contributed to the evolution of hygiene practices. These influences led to the incorporation of different bathing methods and herbal remedies into Chinese culture. The Silk Road facilitated the exchange of knowledge about herbs, bathing techniques, and even philosophies about health and hygiene.
Daily Hygiene Routines in Ancient China
Personal Hygiene and Grooming
Personal hygiene in ancient China encompassed more than just bathing; it included a range of grooming practices aimed at maintaining cleanliness and social appearance.
- Oral Hygiene:
- The ancient Chinese used twigs from certain trees (like salix or willow) as primitive toothbrushes and employed various herbal mixtures for fresh breath.
- Body Hygiene:
- Besides bathing, body hygiene also involved using natural oils and perfumes derived from flowers and herbs to enhance scent and maintain cleanliness.
Seasonal Hygiene Practices
Hygiene practices often varied with the seasons. The ancient Chinese recognized the need for different approaches to cleanliness based on climatic conditions:
- Summer:
- More frequent baths were common in the hot months to alleviate discomfort and reduce sweat-related issues.
- Winter:
- During colder months, bathing frequency decreased, but warm herbal baths were favored for their soothing effects.
- Festivals:
- Cleanliness took on heightened significance during festivals, with rituals often including purification through bathing.
Social and Cultural Aspects of Hygiene
The Influence of Confucianism on Hygiene Practices
Confucianism played a vital role in shaping the societal norms around hygiene in ancient China. Confucian ideals emphasized the importance of cleanliness, viewing it as a reflection of moral integrity and personal discipline.
“The gentleman understands what is right; the small man understands what is profitable.” — Confucius
- Cleanliness was linked to one’s moral character, and maintaining hygiene was seen as essential for personal and societal harmony.
Gender Differences in Hygiene Practices
Hygiene practices were often distinct between genders. Traditional expectations dictated that women had specific grooming rituals, focusing on beauty and modesty.
- Women’s Hygiene:
- Women utilized herbal infusions and powders to maintain skin tone and prevent blemishes, reflecting societal standards of beauty.
- Men’s Hygiene:
- Men, on the other hand, focused more on practical aspects of hygiene, such as shaving and grooming facial hair.
The Impact of Hygiene on Health in Ancient China
Preventing Disease Through Hygiene
In ancient China, the connection between cleanliness and health was well understood. Historical texts reveal the importance of maintaining hygiene to prevent diseases:
- Historical Accounts:
- Texts from the Han and Tang dynasties highlight how poor sanitation led to outbreaks of diseases, prompting authorities to enforce public hygiene measures.
Herbal Remedies and Bathing
Ancient Chinese medicine integrated bathing with herbal remedies to promote health. Many believed that certain herbs used in baths had healing properties, contributing to both physical and mental well-being.
- Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM):
- TCM emphasized the balance of body and mind, and bathing with specific herbs was often recommended as part of a holistic approach to health.
Summary of Key Points
Hygiene in ancient China was a multifaceted practice deeply rooted in cultural beliefs, health considerations, and social norms. From the bathing materials and methods used to the philosophical underpinnings of cleanliness, ancient Chinese hygiene reflects a sophisticated understanding of the importance of health and social harmony.
Meta Description: Discover the fascinating bathing practices and hygiene in ancient China, including what ancient Chinese used to bathe and their cultural significance.
References:
- History Defined – Hygiene in Ancient China
https://www.historydefined.net/what-was-hygiene-like-in-ancient-china/