Uncovering the Defining Moments of the 17th Century
The 17th century was a pivotal era in world history, marked by significant political, social, and scientific transformations. This period, spanning from 1601 to 1700, witnessed profound changes that shaped the modern world. In this article, we’ll explore the most crucial events of the 17th century, delve into the social and cultural transformations of the time, and examine how these events influenced future developments.
What Were the Key Events of the 17th Century?

The Rise of Absolutism
Absolutism emerged as a dominant political system in Europe during the 17th century. This form of governance, where a single ruler holds absolute power, was epitomized by monarchs such as Louis XIV of France. Known as the “Sun King,” Louis XIV centralized power, reducing the influence of nobility and asserting control over the state’s affairs. His reign marked the height of absolute monarchy, influencing the political landscape across Europe.
- Louis XIV’s Reign: Louis XIV’s centralized control and the construction of the Palace of Versailles symbolized his absolute power. His governance model set a precedent for future European monarchs.
- Impact on European Politics: The rise of absolutism led to increased centralization of power and the weakening of feudal structures, paving the way for modern nation-states.
The Thirty Years’ War (1618-1648)
The Thirty Years’ War was a devastating conflict that shaped the political and religious landscape of Europe. Originating in the Holy Roman Empire, the war involved a complex web of alliances and conflicts between Protestant and Catholic states.
- Background and Causes: The war began as a struggle between Protestant and Catholic states within the Holy Roman Empire, eventually escalating into a broader European conflict.
- Major Battles and Treaties: Key battles such as the Battle of White Mountain and the Treaty of Westphalia in 1648 were crucial in determining the war’s outcome.
- Consequences: The Treaty of Westphalia marked the end of the war, leading to significant changes in the European political map and laying the foundation for the modern state system.
The English Civil War (1642-1651)
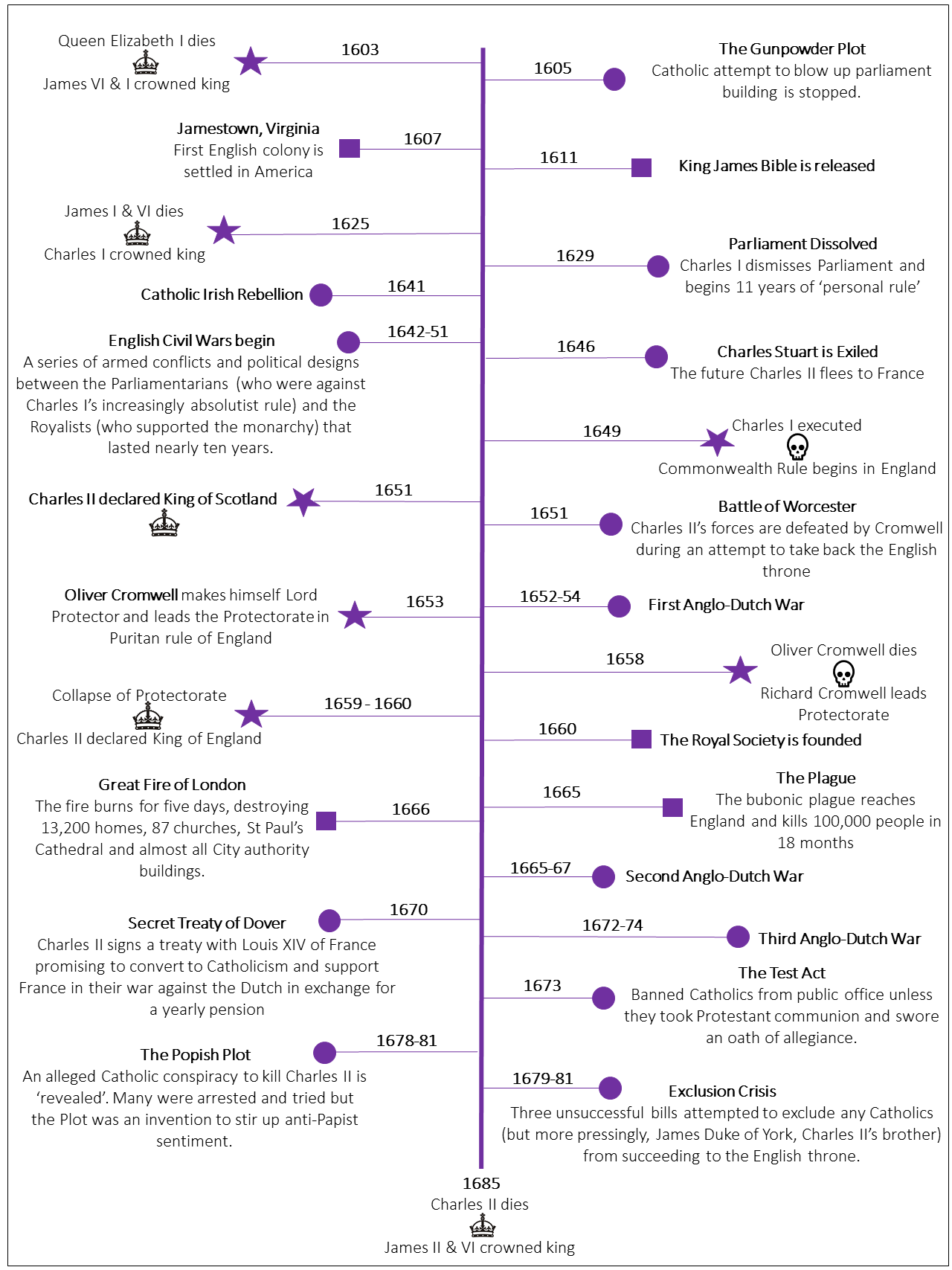
The English Civil War was a pivotal conflict that determined the future of the British monarchy. The struggle between King Charles I and the Parliament, led by figures such as Oliver Cromwell, had far-reaching consequences for British governance.
- Causes and Key Players: Disputes over royal authority and governance led to the outbreak of war. Key figures included King Charles I, who sought to maintain royal prerogative, and Oliver Cromwell, who championed parliamentary sovereignty.
- Major Events and Battles: The war saw significant battles, including the Battle of Naseby. Cromwell’s New Model Army played a decisive role in the conflict.
- Outcomes and Impact: The eventual victory of the Parliamentarians led to the temporary abolition of the monarchy and the establishment of the Commonwealth of England, which profoundly affected the future of British constitutional monarchy.
The Scientific Revolution
The Scientific Revolution was a period of immense intellectual advancement that laid the groundwork for modern science. Key figures such as Galileo Galilei and Isaac Newton revolutionized the understanding of the natural world.
- Overview of Key Figures: Galileo Galilei‘s support for heliocentrism and Isaac Newton‘s formulation of the laws of motion and universal gravitation were groundbreaking.
- Scientific Discoveries and Theories: Major contributions included the development of the scientific method and advancements in physics and astronomy.
- Influence on Modern Science: The Scientific Revolution transformed the approach to scientific inquiry and established principles that continue to underpin scientific research today.
The Development of Colonial Empires
The 17th century was a crucial period for the expansion of European colonial empires. Nations such as Britain, the Netherlands, and France established vast overseas colonies, reshaping global trade and politics.
- European Exploration and Colonization: Explorers and colonizers established key settlements and trade routes in the Americas, Africa, and Asia.
- Key Events in Colonial Expansion: The founding of colonies such as New Amsterdam (modern-day New York) and the establishment of trade monopolies by the Dutch East India Company were significant.
- Effects on Global Trade and Indigenous Populations: The expansion led to increased global trade but also had devastating effects on indigenous peoples through conflict and disease.
Social and Cultural Transformations
Advances in Art and Literature
The 17th century was a vibrant period for art and literature, with notable figures making significant contributions. Rembrandt van Rijn and John Milton are among the most celebrated artists and writers of the era.
- Major Artists and Literary Figures: Rembrandt is renowned for his masterful use of light and shadow, while John Milton‘s epic poem, Paradise Lost, remains a cornerstone of English literature.
- Influences of the Period: The art and literature of the time reflected the dramatic changes and conflicts of the century, often exploring themes of power, religion, and human nature.
- Legacy and Impact: The works produced during this period continue to be studied and admired for their artistic and intellectual depth.
The Rise of Capitalism
The rise of capitalism in the 17th century marked a shift in economic practices and theories. The development of global trade networks and the rise of merchant capitalism played a crucial role in shaping modern economic systems.
- Economic Changes and Trade Development: The expansion of trade routes and the establishment of financial institutions laid the groundwork for modern capitalism.
- Key Economic Theories and Practices: The period saw the rise of mercantilism and early forms of capitalist thought, influencing economic policies and practices.
- Influence on Global Economics: The emergence of capitalist practices transformed global trade and laid the foundation for the modern economic system.
Major Conflicts and Their Impacts
The Franco-Dutch War (1672-1678)
The Franco-Dutch War was a significant conflict between France and the Dutch Republic. The war had profound effects on European politics and alliances.
- Causes and Key Battles: The war was driven by French ambitions to expand its influence and Dutch resistance. Key battles included the Battle of Seneffe.
- Outcomes and Effects: The war ended with the Treaty of Nijmegen, which reshaped the political landscape of Europe and influenced future diplomatic relations.
The Great Turkish War (1683-1699)
The Great Turkish War was a major conflict between the Ottoman Empire and a coalition of European states. The war had lasting implications for European-Turkish relations.
- Background and Major Conflicts: The war began with the Ottoman Empire’s expansion into Central Europe and saw significant battles, including the Battle of Vienna.
- Role of Key Figures: Leaders such as John III Sobieski played crucial roles in the conflict.
- Implications for European-Turkish Relations: The war ended with the Treaty of Karlowitz, which marked a significant shift in power dynamics between Europe and the Ottoman Empire.
Summary of Main Figures
| Name | Role | Significance |
|---|---|---|
| Louis XIV | King of France | Epitome of absolutism, centralized power in France |
| Galileo Galilei | Scientist | Key figure in the Scientific Revolution, supporter of heliocentrism |
| Isaac Newton | Scientist | Formulated the laws of motion and universal gravitation |
| Oliver Cromwell | Parliamentary Leader | Led the Parliamentarians in the English Civil War |
| John III Sobieski | King of Poland | Defeated the Ottomans at the Battle of Vienna |
This comprehensive overview of the 17th century highlights the major events and transformations of the era, providing a detailed exploration of how this pivotal century shaped the modern world.
References:
- History Defined: What Were the Most Important Events of the 17th Century?
https://www.historydefined.net/what-were-the-most-important-events-of-the-17th-century/ - Wikipedia: Louis XIV
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Louis_XIV - Wikipedia: Galileo Galilei
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Galileo_Galilei - Wikipedia: Isaac Newton
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Isaac_Newton - Wikipedia: Oliver Cromwell
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Oliver_Cromwell - Wikipedia: John III Sobieski
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/John_III_Sobieski






