Unveiling Angerboda: The Enigmatic Mother of Norse Monsters
The Mythological Background of Angerboda
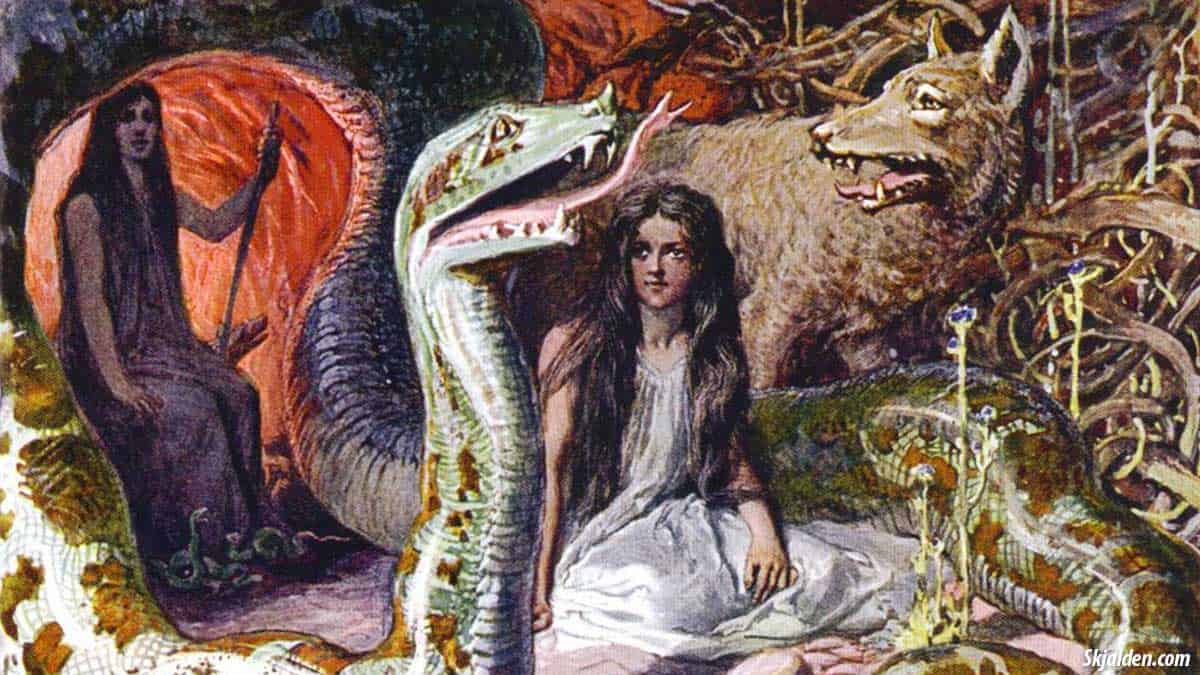
Angerboda, a pivotal figure in Norse mythology, stands as a symbol of power and mystery. Her name, meaning “The Foreboder” or “The One Who Brings Grief,” hints at her dark and complex role within the mythological pantheon. Known primarily as the mother of three significant monsters, Angerboda’s story intertwines with some of the most dramatic and crucial events in Norse lore.
Angerboda’s Origins and Lineage
Angerboda’s origins are deeply rooted in the chaotic and primordial aspects of Norse mythology. She is often identified as a giantess, or Jotunn, who resides in Jotunheim, the land of the giants. Her parentage is somewhat ambiguous, but she is typically linked to the giants of the old world, contrasting with the Aesir gods who reside in Asgard.
Angerboda’s relationship with the gods is marked by conflict and prophecy. She is famously known for her union with Loki, a trickster god whose offspring with Angerboda would come to play critical roles in the mythological narrative. The union of Angerboda and Loki is seen as a catalyst for some of the most significant events leading up to Ragnarok, the end of the world in Norse mythology.
Angerboda’s Offspring: The Norse Monsters
Angerboda’s children with Loki—Fenrir, Jormungandr, and Hel—are central figures in the Norse mythological tradition. Each of these monsters plays a crucial role in the events that shape the cosmic struggle between order and chaos.
Fenrir the Wolf
Fenrir, also known as Fenrisúlfr, is a monstrous wolf with immense strength and a fearsome reputation. According to the myths, Fenrir was foretold to be a destructive force, destined to play a key role in Ragnarok. As he grew, the gods, fearing his power, decided to imprison him to prevent him from causing havoc.
Description and Traits: Fenrir is described as an enormous and fearsome wolf, so strong that the gods had to use enchanted chains to contain him. His boundless strength and ferocity make him a symbol of uncontrollable chaos and destruction.
Significance in Mythology: Fenrir’s fate is intricately tied to the prophecy of Ragnarok. It is said that during this apocalyptic battle, Fenrir will break free from his chains and devour Odin, the chief of the Aesir gods. This event underscores his role as an embodiment of ultimate destruction and chaos.
Jormungandr the Serpent
Jormungandr, or the Midgard Serpent, is another of Angerboda’s monstrous offspring. Unlike Fenrir, Jormungandr is a giant serpent that encircles the earth, representing an immense and ancient threat.
Description and Traits: Jormungandr is described as a serpent so large that it can wrap around the world and bite its own tail. His presence is a constant reminder of the boundaries between chaos and order.
Significance in Mythology: Jormungandr’s role in Norse mythology is closely linked to the events of Ragnarok. The serpent’s battle with Thor, the god of thunder, is one of the epic confrontations predicted to occur during the end times. Jormungandr’s release from the ocean will signal the beginning of the end of the world, emphasizing his role as a harbinger of destruction.
Hel, Goddess of the Underworld
Hel is the third of Angerboda’s children, and her domain is the underworld, where she presides over the souls of the deceased who did not die gloriously in battle.
Description and Traits: Hel is depicted as having a half-living, half-dead appearance, reflecting her role as the ruler of the realm of the dead. Her presence is both a symbol of death and a reminder of the inevitability of mortality.
Significance in Mythology: As the ruler of Helheim, Hel governs over the souls of those who did not earn a place in Valhalla or other honored afterlife realms. Her role in mythology is crucial, as she represents the inevitable end that all must face, making her a significant figure in the narrative of life and death in Norse beliefs.
Angerboda’s Influence and Legacy
Angerboda’s impact on Norse mythology extends beyond her immediate family. Her legacy is a reflection of the complex interplay between chaos and order within the mythological framework.
Symbolism and Cultural Impact
Angerboda symbolizes the primordial forces of chaos and destruction. Her role as the mother of monsters and her connections to the end times reflect the ancient Norse understanding of the cyclical nature of the cosmos. Her children—Fenrir, Jormungandr, and Hel—each embody different aspects of chaos, destruction, and death, emphasizing her integral role in the mythological universe.
Cultural Reflection: Angerboda’s story has influenced various aspects of Norse culture and literature. She is a symbol of the darker, more chaotic forces that balance the more orderly aspects of the mythological world. Her portrayal in sagas and modern interpretations highlights her role as a powerful and enigmatic figure whose influence extends through the ages.
Angerboda in Modern Interpretations
In modern times, Angerboda’s character has seen a resurgence in literature, film, and popular culture. Her role as the mother of mythological monsters has been explored in various adaptations, ranging from fantasy novels to movies.
Contemporary Portrayals: Angerboda is often depicted with a focus on her dark and mysterious qualities, reflecting her role as a bringer of chaos. Modern interpretations frequently emphasize her connection to the monstrous and the apocalyptic, aligning with her traditional representation as a figure of immense power and influence.
Comparison with Other Mythological Figures
Angerboda’s role can be compared to other mythological figures who represent chaos or primordial forces in different cultures. Understanding these parallels can provide a deeper insight into her significance in Norse mythology.
Angerboda and Mythological Mothers

In comparing Angerboda to other mythological mother figures, one might consider figures such as Gaia from Greek mythology or Tiamat from Babylonian myths. Each of these figures represents a form of primordial chaos or creation, reflecting the role of Angerboda as a mother of significant mythological beings.
- Gaia: Like Angerboda, Gaia is a primordial entity whose offspring include powerful and often chaotic figures.
- Tiamat: Represents chaos and creation, much like Angerboda’s role in birthing monsters that embody chaos.
Legacy of Norse Mythological Figures
The legacy of Norse mythological figures, including Angerboda, is evident in their continued presence in modern literature, games, and films. Their stories continue to captivate audiences, reflecting enduring themes of chaos, destruction, and the struggle between order and disorder.
- Influence on Modern Culture: Norse mythological figures have been adapted and reimagined in various forms of media, reflecting their lasting impact on contemporary storytelling and cultural expression.
Meta Description: Explore Angerboda, the mysterious Norse giantess and mother of monsters. Discover her role in Norse mythology and her impact on modern interpretations.
References
- History Defined – Angerboda https://www.historydefined.net/angrboda/
- Wikipedia – Angerboda https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Angerboda